Blog post
Conductive Hearing Loss
Sometimes a problem in the outer or middle ear stops sound waves getting through to the inner ear as well as they should do. It can often be temporary, as a result of a build-up of wax, for example, or an infection that your audiologist can diagnose and treat. Some other outer or middle-ear conditions may require further medical investigation or treatment. Your hearing specialist will refer you to an ear, nose and throat (ENT) doctor if they are unable to treat it themselves.
What Are the Symptoms of Conductive Hearing Loss?
Symptoms of conductive hearing loss can vary depending on the exact cause and severity, but may include or be associated with:
- Muffled hearing
- Sudden or steady loss of hearing
- Full or “stuffy” sensation in the ear
- Dizziness
- Draining of the ear
- Pain or tenderness in the ear
What Are the Treatment Options?
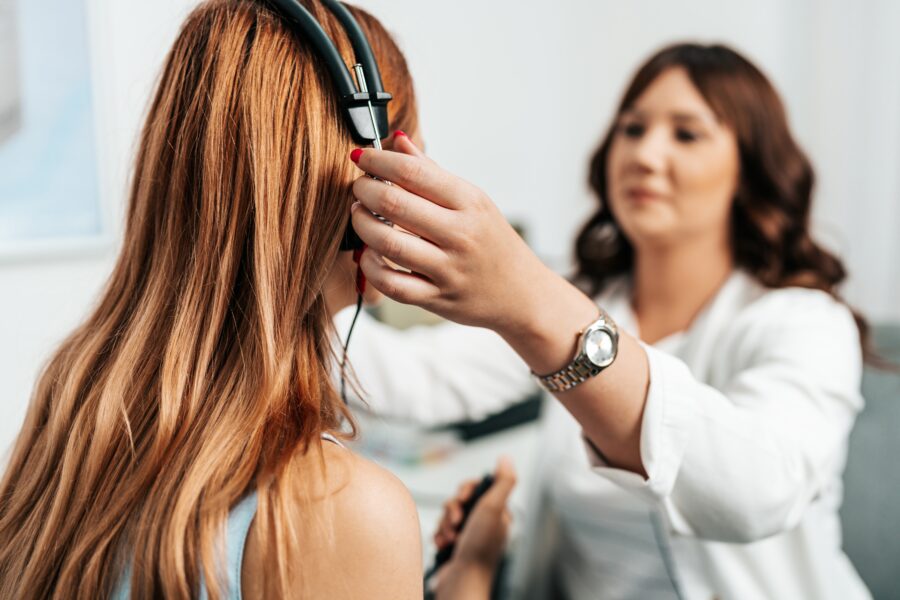
If you are experiencing hearing loss, you should see a hearing specialist, who can make a specific diagnosis for you, and talk to you about treatment options. A critical part of the evaluation will be a hearing test (audiogram) to determine the severity of your loss.