Blog post
Eye strain: What is it, causes and how to relieve and prevent it

Matthew Burford BSc(Hons) Optometry MCOptom - Domiciliary Optician and Professional Services Manager at OutsideClinic
5-7 minute read time
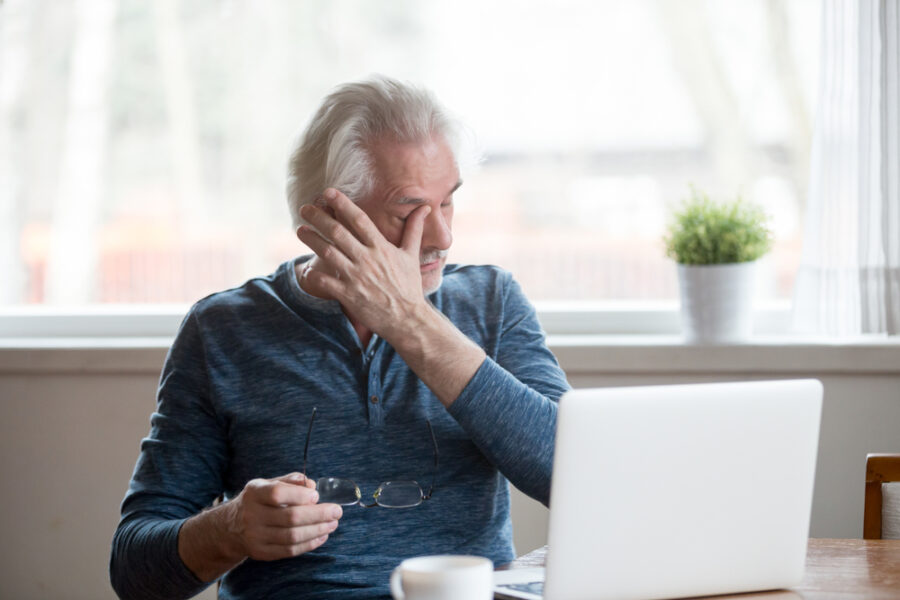
Eye strain, or asthenopia, is a common condition that happens when your eyes get tired from overuse. It often occurs after prolonged activities like reading, driving, or staring at a screen.
For many people, it’s a temporary discomfort, but it can feel quite unpleasant.
What causes eye strain? Why could my eyes feel strained?
- Not wearing glasses or using outdated prescriptions: When your eyes are not properly corrected, they have to work harder to focus, leading to fatigue and strain.
- Tiredness: Fatigue can make your eyes work harder.
- Astigmatism or other eye health issues: Conditions such as astigmatism, hyperopia (farsightedness), myopia (nearsightedness), and presbyopia (age-related difficulty focusing on close objects) can increase strain if left uncorrected. Uncorrected vision problems can increase strain.
- Prolonged screen time: Extended use of digital devices like computers, smartphones, or tablets can cause eye strain, often due to reduced blinking and improper posture.
- Driving: Long hours of focused driving can strain the eyes.
- Reading without breaks: Prolonged reading, especially in dim light, can exacerbate strain.
- Poor workstation setup: Incorrect screen height or posture can increase strain.
- Cold/flu/COVID: Illnesses often affect how your eyes feel, with symptoms like congestion and irritation potentially leading to strain.
- Anxiety: Anxiety can lead to eye strain as a result of muscle tension and prolonged periods of stress.
- Crying: Crying can leave eyes feeling tired and irritated.

What does eye strain feel like?
Eye strain can make your eyes feel achey and tired.
You may notice a sense of heaviness or soreness in and around your eyes.
Many people also struggle to focus, which can make tasks like reading or working on a computer more challenging.

What are the signs and symptoms of eye strain?
Some of the most common signs and symptoms include:
- Headaches, often around the temples or forehead
- Blurred vision
- Dry eyes or excessive tearing
- A burning or stinging sensation in the eyes
- Difficulty focusing
- Sensitivity to light
- Feeling as though your eyes are heavier than usual
What’s digital eye strain?
Digital eye strain, also known as computer vision syndrome, occurs when your eyes feel tired or uncomfortable after extended use of digital devices like computers, smartphones, or tablets.
Reduced blinking, poor posture, and prolonged focus can lead to symptoms such as dry eyes, headaches, blurred vision, and difficulty concentrating.
Can eye strain cause blindness?
Eye strain itself does not cause blindness.
However, persistent discomfort could indicate an underlying eye condition that may require medical attention. If you experience ongoing symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional.
What’s the treatment or management for eye strain?
- Wear glasses if needed: Prescription glasses can help reduce strain. Ensure you have regular eye tests to keep your prescription up to date.
- Take regular breaks: Follow the 20:20:20 rule - every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds.
- Adjust your screen setup: Using proper setups for your workstation, such as ensuring your screen is at eye level, your chair supports good posture, and your keyboard and mouse are positioned for comfort, can significantly reduce strain. Adding an anti-glare filter to your screen can also prevent unnecessary eye strain. Adjusting font size and contrast settings on digital screens can also help.
- Keep your eyes hydrated: Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water, blinking often during focused activities, using a humidifier to maintain moisture in the air (especially during winter), and applying hydrating eye drops as needed can all help prevent dryness and discomfort. Here at OutsideClinic, our Optometrists recommend Thealoz or Hyabak eye drops.
- Improve lighting: Ensure adequate lighting in your workspace to reduce strain.

How long does eye strain last?
Eye strain typically resolves on its own with rest and proper care. For most people, symptoms improve within a few hours or days.
However, you should speak to a healthcare professional if you experience ongoing or severe discomfort.
What other symptoms are linked to eye strain?
Eye strain can sometimes be associated with other symptoms, including:
- Eye twitching: Muscle fatigue from prolonged use can cause involuntary spasms around the eyes.
- Dry eyes: Reduced blinking during focused activities can lead to insufficient lubrication of the eyes.
- Blurred vision: Prolonged strain can temporarily impact your ability to focus, causing blurriness.
- Dizziness and light-headedness: Straining to focus for extended periods can disrupt your sense of balance or cause discomfort due to overexertion of eye muscles.
- Migraines: Eye strain can trigger migraines in individuals prone to them, especially after prolonged screen time or reading.
- Eye floaters: While floaters are not caused by eye strain, their appearance may be more noticeable when your eyes are tired or strained.
- Neck and shoulder pain due to poor posture: If you’re experiencing eye strain, you may find yourself sitting in awkward positions while working or reading to see properly.
When should I see an optician?
You should consult a professional if your symptoms persist. This is particularly important if you experience:
- Severe or recurring headaches
- Persistent blurred vision
- Sensitivity to light
- Pain in or around your eyes
- Sudden onset of new symptoms, such as double vision or extreme light sensitivity
What does it mean if I have eye strain only in one eye?
Eye strain in only one eye could indicate a specific issue with that eye, such as astigmatism or dry eye, or it might be a sign that your glasses prescription is out of date.
Each eye can have different levels of vision, and wearing glasses that don’t correct for these differences can cause one eye to work harder than the other.
What does it mean if my eyes feel strained when I first wake up?
Morning eye strain can result from sleeping with your eyes slightly open, dehydration, or poor-quality sleep.
What’s the best TV for eye strain?
Look for TVs with features like anti-glare screens and adjustable brightness. Using a TV in a well-lit room and sitting at an appropriate distance can also help reduce strain.
Do blue light glasses help reduce eye strain?
Blue light glasses are designed to filter out the blue light emitted by digital screens.
While there is evidence that blue light can interfere with circadian rhythms and sleep, there isn't solid scientific evidence showing that blue light from digital devices causes physical eye damage or strain.

How does screen brightness affect eye strain?
Too much brightness can cause glare and discomfort, while screens that are too dim can make your eyes work harder to focus. Adjust your screen brightness to match the ambient light in your room.

By Matthew Burford BSc(Hons) Optometry MCOptom - Domiciliary Optician and Professional Services Manager at OutsideClinic
Matthew graduated from Aston University in 2004 with a degree in Optometry.